Definition
Optical Measuring Instruments. (in machine building), instruments in which sighting (alignment of the boundaries of the dimension being checked with a reference line or with cross hairs) is done or a dimension is determined by means of a device with an optical principle of operation.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585858357-56ac380e5f9b58b7d00a6c3a.jpg)


Digital tachometer is an optical encoder that determines the angular velocity of a rotating shaft or motor. Digital tachometers are used in different applications such as automobiles, aeroplanes, and medical and instrumentation applications.



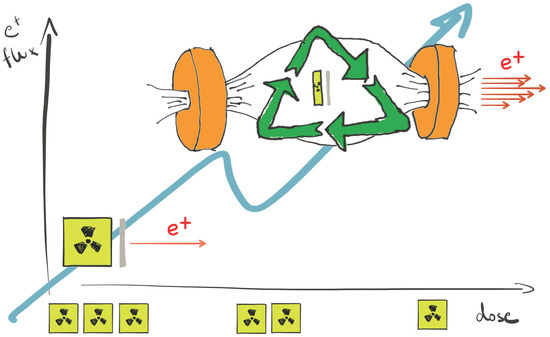
 The properties of the proton beam thus obtained have been analysed and compared with Monte Carlo simulations. The results of this comparison, as well as the experimental measurement of the lateral dose profiles expected at the position of samples are presented. Meaningful dose rates of about 2–3 Gy/min have been obtained. Homogeneous lateral dose profiles, with maximum deviations of 5%, have been measured at a distance of approximately 50 cm in air from the exit window, placing a tungsten scattering foil of 200 μm in the beam path.
The properties of the proton beam thus obtained have been analysed and compared with Monte Carlo simulations. The results of this comparison, as well as the experimental measurement of the lateral dose profiles expected at the position of samples are presented. Meaningful dose rates of about 2–3 Gy/min have been obtained. Homogeneous lateral dose profiles, with maximum deviations of 5%, have been measured at a distance of approximately 50 cm in air from the exit window, placing a tungsten scattering foil of 200 μm in the beam path.
Optical Measuring Instruments. (in machine building), instruments in which sighting (alignment of the boundaries of the dimension being checked with a reference line or with cross hairs) is done or a dimension is determined by means of a device with an optical principle of operation.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585858357-56ac380e5f9b58b7d00a6c3a.jpg)
Surveying Process
The surveying process is a procedural one and, by following these instructions, you should be able to survey an entire stage from beginning to end.
The order of the survey process:
physical setup of survey instruments
configure data collector
- measure and store points
- move to another physical location (if necessary)
- finish measuring points
- export points
The survey process can take anywhere between 1-5 hours depending on the size of the stage and visibility of targets. Stages with wires and lights in the way of the targets will take longer because you will need to move the survey instrument to multiple locations to capture all points.
- Total Station with Reflectorless Mode – this allows the total station to take measurements without the use of a prism or reflective stickers.
- Right Angle Eye Piece – for surveying points overhead, a 90-degree eye piece makes it easier to see the targets.
- Total Station Tripod and Spreaders – the tripod and tripod spreader are important tools. Without these, the survey gun cannot be properly leveled.
- Data Collector – this is a separate piece of hardware that acts like a handheld computer. The Data Collector is able to store and output point data as well as configure the total station.
- Bluetooth Data or Serial Data Cable for Data Collector – for the Data Collector to communicate with the Total Station, you will need either Bluetooth connectivity or a hard wired serial cable connection. We recommend having a cable as Bluetooth often drops out in sound stages.
Digital Tachometer Circuit Operation using Microcontroller and their Types
A digital tachometer is a digital device that measures and indicates the speed of a rotating object. A rotating object may be a bike tyre, a car tyre or a ceiling fan, or any other moter , and so on. A digital tachometer circuit comprises LCD or LED read out and a memory for storage. Digital tachometers are more common these days and they provide numerical readings instead of dials and needles.

Digital tachometer is an optical encoder that determines the angular velocity of a rotating shaft or motor. Digital tachometers are used in different applications such as automobiles, aeroplanes, and medical and instrumentation applications.
Height gauge
A height gauge is a measuring device used for determining the height of objects, and for marking of items to be worked on.These measuring tools are used in metal working or metrology to either set or measure vertical distances; the pointer is sharpened to allow it to act as a scriber and assist in marking out work pieces.
Devices similar in concept, with lower resolutions, are used in health care settings (HEALTH CLINICS , SURGERIES,) to find the height of people, in which context they are called stadiometers .
Height gauges may also be used to measure the height of an object by using the underside of the scriber as the datum. The datum may be permanently fixed or the height gauge may have provision to adjust the scale, this is done by sliding the scale vertically along the body of the height gauge by turning a fine feed screw at the top of the gauge;

then with the scriber set to the same level as the base, the scale can be matched to it. This adjustment allows different scribers or probes to be used, as well as adjusting for any errors in a damaged or resharpened probe.
In the TOOLROOM, the distinction between a height gauge and a surface gauge is that a height gauge has a measuring head (whether verner, fine rack and pinion with dial , or linear encoder with digital display), whereas a surface gauge has only a scriber point. Both are typically used on plants and have a heavy base with an accurately flat, smooth underside.
A feasibility study of an experimental setup for the irradiation of biological samples at the cyclotron facility installed at the National Centre of Accelerators (Seville, Spain) is presented. This cyclotron, which counts on an external beam line for interdisciplinary research purposes, produces an 18 MeV proton beam, which is suitable for the irradiation of mono-layer cultures for the measurement of proton cell damages and Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) at energies below the beam nominal value. Measurements of this kind are of interest for proton therapy, since the variation of proton RBE at the distal edge of the Bragg curve may have implications in clinical proton therapy treatments.

. In the following, the characteristics of the beam line and the solutions implemented for the irradiation of biological samples are described. When dealing with the irradiation of cell cultures, low beam intensities and broad homogeneous irradiation fields are required, in order to assure that all the cells receive the same dose with a suitable dose rate. At the cyclotron, these constraints have been achieved by completely defocusing the beam, intercepting the beam path with tungsten scattering foils and varying the exit-window-to-sample distance.
 The properties of the proton beam thus obtained have been analysed and compared with Monte Carlo simulations. The results of this comparison, as well as the experimental measurement of the lateral dose profiles expected at the position of samples are presented. Meaningful dose rates of about 2–3 Gy/min have been obtained. Homogeneous lateral dose profiles, with maximum deviations of 5%, have been measured at a distance of approximately 50 cm in air from the exit window, placing a tungsten scattering foil of 200 μm in the beam path.
The properties of the proton beam thus obtained have been analysed and compared with Monte Carlo simulations. The results of this comparison, as well as the experimental measurement of the lateral dose profiles expected at the position of samples are presented. Meaningful dose rates of about 2–3 Gy/min have been obtained. Homogeneous lateral dose profiles, with maximum deviations of 5%, have been measured at a distance of approximately 50 cm in air from the exit window, placing a tungsten scattering foil of 200 μm in the beam path.
Optical measurement instrument I admire this article for the well-researched content and excellent wording. I got so involved in this material that I couldn’t stop reading. I am impressed with your work and skill. Thank you so much.
ReplyDelete