Definition :-
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Active suspension is a type of automotivesuspension that controls the vertical movement of the wheels relative to the chassis or vehicle body with an onboard system, rather than in passive suspension where the movement is being determined entirely by the road surface.

With respect to weight, energy consumption, and cost constraints, hydro-active suspension system is a suitable choice for improving vehicle ride comfort while keeping its handling. The aim of sensors selection is determining number, location, and type of sensors, which are the best for control purposes.
 Selection of sensors is related to the selection of measured variables (outputs). Outputs selection may limit performance and also affect reliability and complexity of control systems. In the meanwhile, hardware, implementation, maintenance, and repairing costs can be affected by this issue. In this study, systematic methods for selecting the viable outputs for hydro-active suspension system of a passenger car are implemented.
Selection of sensors is related to the selection of measured variables (outputs). Outputs selection may limit performance and also affect reliability and complexity of control systems. In the meanwhile, hardware, implementation, maintenance, and repairing costs can be affected by this issue. In this study, systematic methods for selecting the viable outputs for hydro-active suspension system of a passenger car are implemented.

Having joint robust stability and nominal performance of the closed loop is the main idea in this selection. In addition, it is very important to use these methods as a complementation for system physical insights, not supersedes. So, in the first place the system is described and the main ideas in ride comfort control are addressed. An 8 degrees of freedom model of vehicle with passive suspension system is derived and validated. Both linear and nonlinear models of the car which is equipped with hydro-active subsystem are derived.
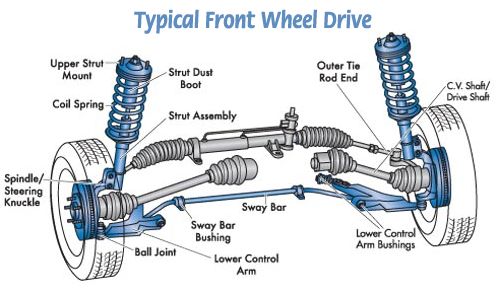
After selecting the outputs, for benefiting from minimum loop interactions, the control configuration is systematically determined. The main goal of selecting control configuration is assessing the possibility of achieving a decentralized control configuration.
 Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.
Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.

 It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing.
It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing.


Michelin’s Active Wheel technology has been around for the past couple of years but actual applications of the electronic powertrain and handling management system are still hard to come by. Over the years the technology has been showcased in a number of concepts, and at this week’s Paris Motor Show Michelin unveiled the latest generation of its innovative design in the new Volage electric roadster concept from Monaco’s Venturi.

The Active Wheel is essentially a standard wheel that houses a pair of electric motors. One of the motors spins the wheel and transmits power to the ground, while the other acts as an active suspension system to improve comfort, handling and stability. The system is designed for battery or fuel-cell powered electric vehicles, and the technology is such that a vehicle equipped with it will no longer need any gearbox, clutch, transmission shaft, universal joint or anti-roll bar.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Active suspension is a type of automotivesuspension that controls the vertical movement of the wheels relative to the chassis or vehicle body with an onboard system, rather than in passive suspension where the movement is being determined entirely by the road surface.
With respect to weight, energy consumption, and cost constraints, hydro-active suspension system is a suitable choice for improving vehicle ride comfort while keeping its handling. The aim of sensors selection is determining number, location, and type of sensors, which are the best for control purposes.
Having joint robust stability and nominal performance of the closed loop is the main idea in this selection. In addition, it is very important to use these methods as a complementation for system physical insights, not supersedes. So, in the first place the system is described and the main ideas in ride comfort control are addressed. An 8 degrees of freedom model of vehicle with passive suspension system is derived and validated. Both linear and nonlinear models of the car which is equipped with hydro-active subsystem are derived.

After selecting the outputs, for benefiting from minimum loop interactions, the control configuration is systematically determined. The main goal of selecting control configuration is assessing the possibility of achieving a decentralized control configuration.
 Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.
Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.
BUILD 7128 – SUBFRAME AND SUSPENSION
Earlier installments of Build128 have taken you through, step-by-step, in how we perform some of the processed we undertake as we construct our cars. From the tub chassis, to the exterior panels, to the preparation and paint stages of the build.
As with our last instalment – the koenigsegg engine t– we’re going to talk in coming instalments about why we do things the way we do, rather than concentrating on how.
 It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing.
It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing. 
While all that’s happening, the tub chassis moves along to Station 5, at which point the chassis is prepared to receive the engine, gearbox and front/rear subframes and suspension.Technicians on Station 5 prepare the chassis for the subframe by fitting a lot of the ancillary items to the chassis. In the photo below, you can see that heat-shields have been fitted, along with the battery and other fittings
Michelin’s Active Wheel technology has been around for the past couple of years but actual applications of the electronic powertrain and handling management system are still hard to come by. Over the years the technology has been showcased in a number of concepts, and at this week’s Paris Motor Show Michelin unveiled the latest generation of its innovative design in the new Volage electric roadster concept from Monaco’s Venturi.
The Active Wheel is essentially a standard wheel that houses a pair of electric motors. One of the motors spins the wheel and transmits power to the ground, while the other acts as an active suspension system to improve comfort, handling and stability. The system is designed for battery or fuel-cell powered electric vehicles, and the technology is such that a vehicle equipped with it will no longer need any gearbox, clutch, transmission shaft, universal joint or anti-roll bar.
Active Wheel’s compact drive motor and integrated suspension system has also enabled designers to fit a standard brake disc between the motors, which means the braking, drive and suspension components are all fitted within the single wheel.Depending on the amount of power or type of usage desired, a given vehicle may feature up to four Active Wheels for AWD traction.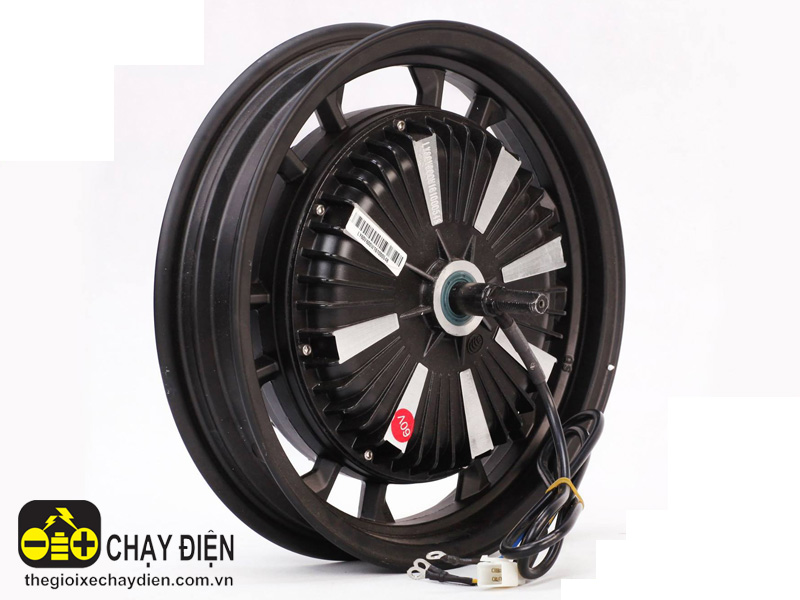 The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.
The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.
 The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.
The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.
No comments:
Post a Comment