Definitions
internal combustion engine a type of engine that is used for most vehicles : an engine in which the fuel is burned within engine cylinders....

Here, the fuel is burnt inside the cylinder of the engine. Chemical energy of the fuel is converted to thermal energy and thermal energy is converted to mechanical energy, which moves the piston up and down inside the cylinder. Power from the piston is transmitted to the crankshaft which is ultimately transmitted to the wheels via a transmission system.Modern automobiles use internal combustion engines for propulsion.

An Internal Combustion Engine (IC Engine) is a type of combustion engine that converts chemical energy into thermal energy, to produce useful mechanical work. In an IC engine, combustion chamber is an integral part of the working fluid circuit.
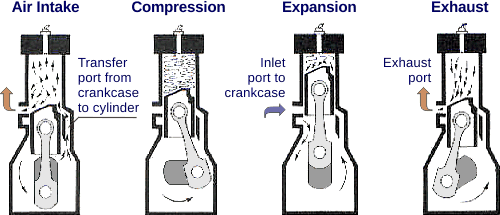
Reciprocating internal combustion engines—a subclass of heat engines—can be operated in the four- and two-stroke cycles. In each case, the engine may be equipped with either a spark-ignited (SI) or a compression-ignited (CI) combustion system. A number of other engine classifications are possible, based on engine mobility, application, fuel, configuration, and other design parameters.  The combustion process can be theoretically modeled by applying laws of mass and energy conservation to the processes in the engine cylinder. Basic design and performance parameters in internal combustion engines include compression ratio, swept volume, clearance volume, power output, indicated power, thermal efficiency, indicated mean effective pressure, brake mean effective pressure, specific fuel consumption, and more.
The combustion process can be theoretically modeled by applying laws of mass and energy conservation to the processes in the engine cylinder. Basic design and performance parameters in internal combustion engines include compression ratio, swept volume, clearance volume, power output, indicated power, thermal efficiency, indicated mean effective pressure, brake mean effective pressure, specific fuel consumption, and more.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Feasibility of technology and operational necessities
- Status of the technology and its future market potential
- Contribution of the technology to protection of the environment
- Climate
- Financial requirements and costs
- References
Direct fuel injection is a technique that allows gasoline and diesel engines to run more fuel efficient. Direct injection techniques are already commonly used in modern diesel engines and are becoming more and more established for gasoline engines. Direct injection engines can lower the CO2 emission of the vehicle by about 15% with low extra costs compared to other techniques leading to similar CO2 emission reduction.
 However, still two thirds of all gasoline powered internal combustion engine vehicles which are sold worldwide are equipped with an internal combustion engine with indirect injection. Direct injection in diesel engines leads to small reductions in NOx and particulate matter emissions which affect local air quality. However, direct injection in gasoline engines can lead to a small increase of NOx and particulate emissions..
However, still two thirds of all gasoline powered internal combustion engine vehicles which are sold worldwide are equipped with an internal combustion engine with indirect injection. Direct injection in diesel engines leads to small reductions in NOx and particulate matter emissions which affect local air quality. However, direct injection in gasoline engines can lead to a small increase of NOx and particulate emissions..
No comments:
Post a Comment