DEFINITION :
 The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses
The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses
. The loss of stability manifests itself by a groove running in a direction perpendicular to the larger principal stress. In this groove local strains begin to concentrate gradually. In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...
In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...


New flexible and hybrid material forming processes
Process modelling and optimisation
Material characterisation, constitutive models, formability and fracture
Friction stir welding and processing of lightweight materials
Tribological behaviour in bulk and sheet forming processes
 The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses
The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses . The loss of stability manifests itself by a groove running in a direction perpendicular to the larger principal stress. In this groove local strains begin to concentrate gradually.
 In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...
In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...
Roll forming, also spelled rollforming, is a type of rolling involving the continuous bending of a long strip of sheet metal (typically coiled steel) into a desired cross-section. The strip passes through sets of rolls mounted on consecutive stands, each set performing only an incremental part of the bend, until the desired cross-section (profile) is obtained. Roll forming is ideal for producing constant-profile parts with long lengths and in large quantities.
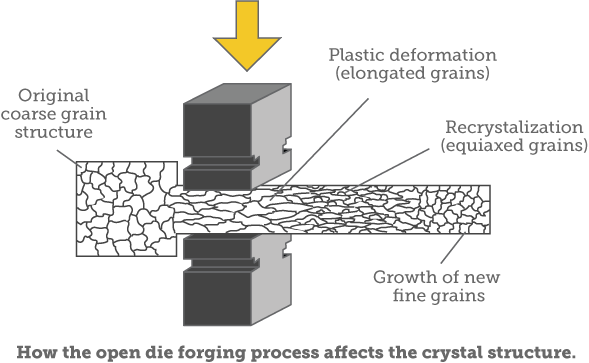
Forging defined
At its most basic level, forging is the process of forming and shaping metals through the use of hammering, pressing or rolling. The process begins with starting stock, usually a cast ingot (or a "cogged" billet which has already been forged from a cast ingot), which is heated to its plastic deformation temperature, then upset or "kneaded" between dies to the desired shape and size.

Advanced Manufacturing Technology Research Group
In close collaboration with academic and industrial partners and with a focus for aerospace, automotive and medical application, the research team carries out fundamental and applied research in the following areas:
No comments:
Post a Comment