MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Journey towards excellent.
Monday, 19 June 2023
Sunday, 18 June 2023
MACHINE GEARS(TRANSMISSION SYSTEM)
There are many types of GEARS such as spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, worm gears, gear rack so many .These can be broadly classified by looking at the positions of axes such as parallel shafts, intersecting shafts and non-intersecting shafts.
If we are discussing about types of gears then it can be classified based on the axis of the shaft, on the basis of the velocity of the gear, on the basis of types of gearing and the last is on the basis of the position of teeth on gear surfaces.
If you talk about the transmission system on vehicle, you surely need to also discuss car gears. Gears are an important component in the engine that makes the vehicle move. Along with its development, the types of gears on cars are increasingly diverse. To find out more about the types and functions of car gears, see the explanation below.
All of us will learn to drive in a car with manual transmission. As driving instructors, we always find that before teaching how to use something, it’s often beneficial to provide a basic understanding of how it works. In this tutorial, we shall provide a basic example of how manual car gears work.
Move the gearstick into neutral in car gears. This is the middle position that feels free when moved from side to side. The vehicle is considered out of gear when:[5]
The gearstick is in the neutral position, and/or
The clutch pedal is fully depressed.
Don’t try to use the gearstick without having the clutch pedal depressed, because it simply won't work.
Monday, 19 November 2018
FORMING
 The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses
The process of the loss of stability is analysed for sheet metal subjected to biaxial tension when the ratio of the principal stresses . The loss of stability manifests itself by a groove running in a direction perpendicular to the larger principal stress. In this groove local strains begin to concentrate gradually.
 In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...
In the initial stage of the process the deepening of the groove is associated with a gradually fading strain in the regions adjacent to the groove. This fading strain attains a certain limiting value ...
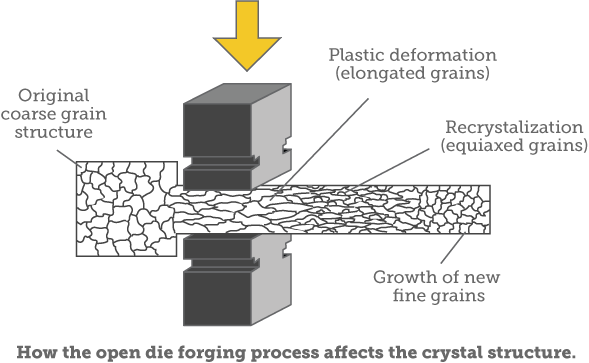
Forging defined

FORGING
Hot forging and cold forging are two different metal forming processes that deliver similar results. Forging is the process of deforming metal into a predetermined shape using certain tools and equipment—deformation is accomplished using hot,cold, or even warm forging processes.
Cold and Hot Forging: An Overview
Forging is a metal shaping process in which a malleable metal part, known as a blank, billet or work-piece, is worked to a predetermined shape by one or more processes such as hammering, upsetting, pressing, rolling and so forth. Cold forming is a precision category of forging which does the same thing without heating of the material (room temperature), or removal of material
WELDING DEFECT

To avoid undercut, welder and welding inspector must observe initial weld lap to see whether the current setting is appropriate. Post welding inspection can be tricky since welder can cover undercut by running another lap using lower grade welding electrode and low current. Undercut is dangerous because it amplifies the stress flow due to reduction in section area and stress concentration of the notch form.

Troubleshooting Weld Defects
Like any portion of the manufacturing or fabrication process, the welding operation is subject to human error from time to time. When weld defects occur as a result of a problem with welding operator's technique or poor equipment settings, it can cause costly downtime and rework, not to mention, frustration.
When a weld defect appears, it's important for welding operators to have the knowledge they need to rectify the situation as quickly as possible. Faster troubleshooting leads to greater opportunities to add value to the welding operation — through increased productivity and quality improvements.

Cold Cracks in Fillet Welds
VARIATIONS OF COLD CRACKS

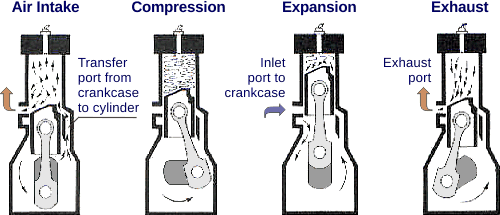
IC ENGINE


- Introduction
- Feasibility of technology and operational necessities
- Status of the technology and its future market potential
- Contribution of the technology to protection of the environment
- Climate
- Financial requirements and costs
- References
 However, still two thirds of all gasoline powered internal combustion engine vehicles which are sold worldwide are equipped with an internal combustion engine with indirect injection. Direct injection in diesel engines leads to small reductions in NOx and particulate matter emissions which affect local air quality. However, direct injection in gasoline engines can lead to a small increase of NOx and particulate emissions..
However, still two thirds of all gasoline powered internal combustion engine vehicles which are sold worldwide are equipped with an internal combustion engine with indirect injection. Direct injection in diesel engines leads to small reductions in NOx and particulate matter emissions which affect local air quality. However, direct injection in gasoline engines can lead to a small increase of NOx and particulate emissions..Green logistics
Green logistics describes all attempts to measure and minimize the ecological impact of logistics activities. This includes all activities of the forward and reverse flows of products, information and services between the point of origin and the point of consumption.

Logistics is the integrated management of all the activities required to move products through the supply chain. For a typical product this supply chain extends from a raw material source through the production and distribution system to the point of consumption and the associated reverse logistics. The logistical activities comprise freight transport, storage, inventory management, materials handling and all the related information processing.
Saturday, 17 November 2018
ELECTRICAL TRANSPARENCY
Transparent conducting oxides (TCOs), which have high transparency through the visible spectrum and high electrical conductivity are already being used in numerous applications. ... A thin conducting layer on or in between the glass panes achieves this.


 "It must seem counterintuitive to many people, that ionic conductors could be used in a system that requires very fast actuation, like our speaker," says Sun. "Yet by exploiting the rubber layer as an insulator, we're able to control the voltage at the interfaces where the gel connects to the electrodes, so we don't have to worry about unwanted chemical reactions.
"It must seem counterintuitive to many people, that ionic conductors could be used in a system that requires very fast actuation, like our speaker," says Sun. "Yet by exploiting the rubber layer as an insulator, we're able to control the voltage at the interfaces where the gel connects to the electrodes, so we don't have to worry about unwanted chemical reactions. 

Power Minister Launches App For Transparency In Due To Gencos From Discoms
The power ministry on Tuesday launched a web application that seeks to bring transparency in dues of power generators from power distribution companies. The app—christened Prapti (payment ratification and analysis in power procurement for bringing transparency in involving of generators—will bring transparency in the payments due to power producers from power distribution companies, power minister R K Singh said. The minister said health of power generator companies was a concern. “This app will go a long way in addressing it. Prompt payments will make generators healthier,” he said, adding this will also enable the banks to recover dues in time.
TRANSPARENCY
Transparency is woven into the fabric of everything we do.
 Information about our investment philosophy, process and fee structure is freely available, as are performance data for your portfolio. We share the underlying rationale for our recommendations, as well as your other options. There are no “black boxes,” and we strive to make our regular reporting clear, straightforward and easy to understand.
Information about our investment philosophy, process and fee structure is freely available, as are performance data for your portfolio. We share the underlying rationale for our recommendations, as well as your other options. There are no “black boxes,” and we strive to make our regular reporting clear, straightforward and easy to understand.
In addition to routine reports and our client portal, you’ll find that we frequently share market observations, analysis and insights through our own client communications. We hold client events to encourage discussion and dialogue, and we love to hear from clients whenever they want to talk or have a question.
ACTIVE ELECTRICALLY CONTROLLED SUSPENSION
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Active suspension is a type of automotivesuspension that controls the vertical movement of the wheels relative to the chassis or vehicle body with an onboard system, rather than in passive suspension where the movement is being determined entirely by the road surface.
With respect to weight, energy consumption, and cost constraints, hydro-active suspension system is a suitable choice for improving vehicle ride comfort while keeping its handling. The aim of sensors selection is determining number, location, and type of sensors, which are the best for control purposes.
Having joint robust stability and nominal performance of the closed loop is the main idea in this selection. In addition, it is very important to use these methods as a complementation for system physical insights, not supersedes. So, in the first place the system is described and the main ideas in ride comfort control are addressed. An 8 degrees of freedom model of vehicle with passive suspension system is derived and validated. Both linear and nonlinear models of the car which is equipped with hydro-active subsystem are derived.
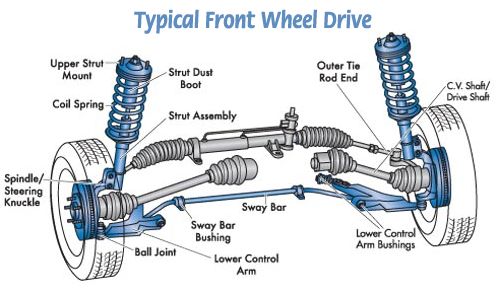
After selecting the outputs, for benefiting from minimum loop interactions, the control configuration is systematically determined. The main goal of selecting control configuration is assessing the possibility of achieving a decentralized control configuration.
 Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.
Finally, the system behavior is controlled by a decentralized proportional–integral–differential (PID) controller. The results indicate the efficiency of the controlled hydro-active suspension system in comparison with the passive system.
BUILD 7128 – SUBFRAME AND SUSPENSION
 It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing.
It’s one thing to tell you that a guy screws a part in to point ‘A’ on the chassis. It’s a different thing, and a more imhportant thing, to tell you what that part does and why it exists.To our subframe and suspension, then…..At this point in production, the panels have been removed from the car at the end of Station 2 and are sent to Station 3/4 for preparation, paint and polishing. 
Michelin’s Active Wheel technology has been around for the past couple of years but actual applications of the electronic powertrain and handling management system are still hard to come by. Over the years the technology has been showcased in a number of concepts, and at this week’s Paris Motor Show Michelin unveiled the latest generation of its innovative design in the new Volage electric roadster concept from Monaco’s Venturi.
The Active Wheel is essentially a standard wheel that houses a pair of electric motors. One of the motors spins the wheel and transmits power to the ground, while the other acts as an active suspension system to improve comfort, handling and stability. The system is designed for battery or fuel-cell powered electric vehicles, and the technology is such that a vehicle equipped with it will no longer need any gearbox, clutch, transmission shaft, universal joint or anti-roll bar.
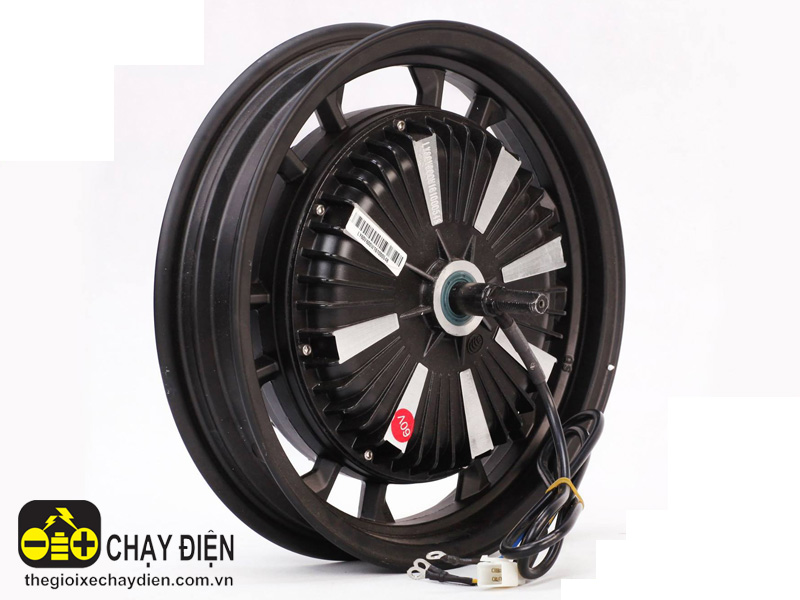 The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.
The system also allows torque from the motors to be electronically controlled for each individual wheel independently. The results are similar to the effects of an active differential, allowing a vehicle with Active Wheel technology to make much faster turns in poor conditions than traditional shaft-driven vehicles.For the suspension, an electric motor controls an actuator connected to a damping system with varying levels of firmness. This unique system features extremely fast response time—just 3/1000ths of a second and all pitching and rolling motions are automatically corrected.